CipherScan
Cipherscan tests the ordering of the SSL/TLS ciphers on a given target, for all major versions of SSL and TLS. It also extracts some certificates informations, TLS options, OCSP stapling and more. Cipherscan is a wrapper above the openssl s_client command line.
Cipherscan is meant to run on all flavors of unix. It ships with its own built of OpenSSL for Linux/64 and Darwin/64. On other platform, it will use the openssl version provided by the operating system (which may have limited ciphers support), or your own version provided in the -o command line flag.
Examples
Basic test:
$ ./cipherscan google.com
...................
Target: google.com:443
prio ciphersuite protocols pfs curves
1 ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305 TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
2 ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
3 ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
4 ECDHE-RSA-RC4-SHA SSLv3,TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
5 AES128-GCM-SHA256 TLSv1.2 None None
6 AES128-SHA256 TLSv1.2 None None
7 AES128-SHA TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 None None
8 RC4-SHA SSLv3,TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 None None
9 RC4-MD5 SSLv3,TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 None None
10 ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
11 ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384 TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
12 ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA SSLv3,TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
13 AES256-GCM-SHA384 TLSv1.2 None None
14 AES256-SHA256 TLSv1.2 None None
15 AES256-SHA SSLv3,TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 None None
16 ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256 TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
17 ECDHE-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA SSLv3,TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
18 DES-CBC3-SHA SSLv3,TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 None None
Certificate: trusted, 2048 bit, sha1WithRSAEncryption signature
TLS ticket lifetime hint: 100800
OCSP stapling: not supported
Cipher ordering: server
Testing STARTTLS:
darwin$ $ ./cipherscan --curves -starttls xmpp jabber.ccc.de:5222
................................
Target: jabber.ccc.de:5222
prio ciphersuite protocols pfs curves
1 ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
2 ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384 TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
3 ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
4 DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 TLSv1.2 DH,1024bits None
5 DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256 TLSv1.2 DH,1024bits None
6 DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 DH,1024bits None
7 DHE-RSA-CAMELLIA256-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 DH,1024bits None
8 AES256-GCM-SHA384 TLSv1.2 None None
9 AES256-SHA256 TLSv1.2 None None
10 AES256-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 None None
11 CAMELLIA256-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 None None
12 ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
13 ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256 TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
14 ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 ECDH,P-256,256bits prime256v1
15 DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 TLSv1.2 DH,1024bits None
16 DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256 TLSv1.2 DH,1024bits None
17 DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 DH,1024bits None
18 DHE-RSA-SEED-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 DH,1024bits None
19 DHE-RSA-CAMELLIA128-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 DH,1024bits None
20 AES128-GCM-SHA256 TLSv1.2 None None
21 AES128-SHA256 TLSv1.2 None None
22 AES128-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 None None
23 SEED-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 None None
24 CAMELLIA128-SHA TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 None None
Certificate: UNTRUSTED, 2048 bit, sha1WithRSAEncryption signature
TLS ticket lifetime hint: None
OCSP stapling: not supported
Cipher ordering: client
Curves ordering: server
Curves fallback: False
Exporting to JSON with the -j command line option:
$ ./cipherscan --curves -j www.ebay.com | j
{
"curves_fallback": "False",
"serverside": "True",
"target": "www.ebay.com:443",
"utctimestamp": "2015-04-03T14:54:31.0Z",
"ciphersuite": [
{
"cipher": "AES256-SHA",
"ocsp_stapling": "False",
"pfs": "None",
"protocols": [
"TLSv1",
"TLSv1.1",
"TLSv1.2"
],
"pubkey": [
"2048"
],
"sigalg": [
"sha1WithRSAEncryption"
],
"ticket_hint": "None",
"trusted": "True"
},
{
"cipher": "ECDHE-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA",
"curves": [
"prime256v1",
"secp384r1",
"secp224r1",
"secp521r1"
],
"curves_ordering": "server",
"ocsp_stapling": "False",
"pfs": "ECDH,P-256,256bits",
"protocols": [
"TLSv1",
"TLSv1.1",
"TLSv1.2"
],
"pubkey": [
"2048"
],
"sigalg": [
"sha1WithRSAEncryption"
],
"ticket_hint": "None",
"trusted": "True"
}
]
}
Analyzing configurations
The motivation behind cipherscan is to help operators configure good TLS on their
endpoints. To help this further, the script analyze.py compares the results of
a cipherscan with the TLS guidelines from https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS
and output a level and recommendations.
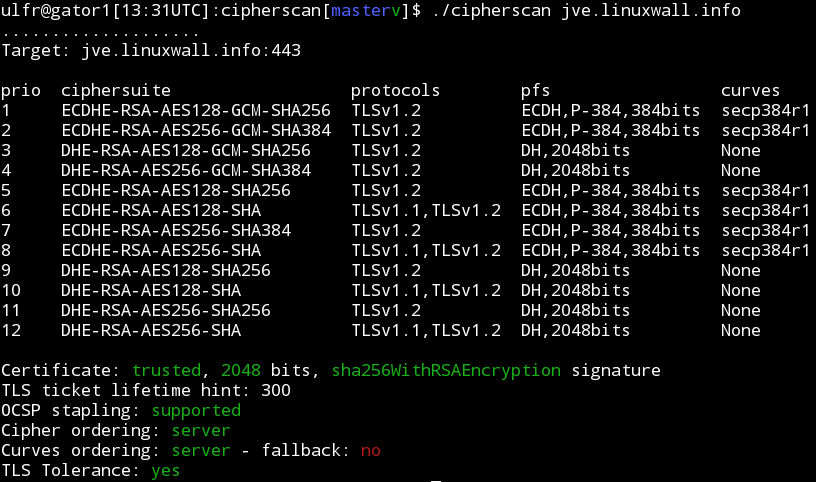
$ ./analyze.py -t jve.linuxwall.info
jve.linuxwall.info:443 has intermediate tls
Changes needed to match the old level:
* consider enabling SSLv3
* add cipher DES-CBC3-SHA
* use a certificate with sha1WithRSAEncryption signature
* consider enabling OCSP Stapling
Changes needed to match the intermediate level:
* consider enabling OCSP Stapling
Changes needed to match the modern level:
* remove cipher AES128-GCM-SHA256
* remove cipher AES256-GCM-SHA384
* remove cipher AES128-SHA256
* remove cipher AES128-SHA
* remove cipher AES256-SHA256
* remove cipher AES256-SHA
* disable TLSv1
* consider enabling OCSP Stapling
In the output above, analyze.py indicates that the target jve.linuxwall.info
matches the intermediate configuration level. If the administrator of this site
wants to reach the modern level, the items that failed under the modern tests
should be corrected.
analyze.py does not make any assumption on what a good level should be. Sites
operators should know what level they want to match against, based on the
compatibility level they want to support. Again, refer to
https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS for more information.
Note on Nagios mode:
analyse.py can be ran as a nagios check with --nagios. The exit code will
then represent the state of the configuration:
- 2 (critical) for bad tls
- 1 (warning) if it doesn't match the desired level
- 0 (ok) if it matches. cipherscan can take more than 10 seconds to complete. To alleviate any timeout issues, you may want to run it outside of nagios, passing data through some temporary file.
OpenSSL
Cipherscan uses a custom release of openssl for linux 64 bits and darwin 64 bits. OpenSSL is build from a custom branch maintained by Peter Mosmans that includes a number of patches not merged upstream. It can be found here: https://github.com/PeterMosmans/openssl
You can build it yourself using following commands:
git clone https://github.com/PeterMosmans/openssl.git --depth 1 -b 1.0.2-chacha
cd openssl
./Configure zlib no-shared experimental-jpake enable-md2 enable-rc5 \
enable-rfc3779 enable-gost enable-static-engine linux-x86_64
make depend
make
make report
The statically linked binary will be apps/openssl.
Contributors
- Julien Vehent julien@linuxwall.info (original author)
- Hubert Kario hkario@redhat.com (co-maintainer)
- Pepi Zawodsky git@maclemon.at
- Michael Zeltner m@niij.org
- Peter Mosmans support@go-forward.net
- Vincent Riquer v.riquer@b2f-concept.com
- Christian Stadelmann
- Simon Deziel simon.deziel@gmail.com
- Aaron Zauner azet@azet.org
- Mike mikedawg@gmail.com
- Phil Cohen phlipper@users.noreply.github.com
- Samuel Kleiner sam@firstbanco.com
- Richard Soderberg https://twitter.com/floatingatoll
- Adam Crosby adamcrosby@users.noreply.github.com